Chess is a game of strategy and skill. Learning the rules of movement is essential.
Chess has been a beloved game for centuries. It challenges the mind and brings joy to players worldwide. Understanding how each piece moves is crucial for success. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to improve, knowing these rules can elevate your game.
In this post, we’ll explore the fundamental rules of chess movement. You’ll learn how each piece navigates the board. This knowledge will help you plan your moves better and anticipate your opponent’s strategy. Ready to dive into the world of chess? Let’s begin with the basics.
Introduction To Chess
Chess is a classic game that has been enjoyed for centuries. It is a game of strategy, skill, and foresight. Players use 16 pieces each to outsmart their opponent. The game is played on a square board with 64 squares. Each piece moves differently. Understanding the rules is crucial to play well. Let’s dive into the basics.
Brief History
Chess has a rich history. It originated in India around the 6th century. The game was called “Chaturanga” at that time. It then spread to Persia and became known as “Shatranj”. Later, it reached Europe and evolved into the game we know today. Chess has been a favorite pastime for many cultures. It has also been a tool for teaching strategic thinking.
Objective Of The Game
The main goal in chess is to checkmate your opponent’s king. This means the king is in a position where it cannot escape capture. Each player aims to protect their own king while attacking their opponent’s king. The game also involves capturing pieces, controlling the board, and planning several moves ahead. Here is a quick overview of the pieces and their movements:
| Piece | Movement |
|---|---|
| King | One square in any direction |
| Queen | Any number of squares in any direction |
| Rook | Any number of squares vertically or horizontally |
| Bishop | Any number of squares diagonally |
| Knight | Moves in an ‘L’ shape: two squares in one direction and then one square perpendicular |
| Pawn | Moves one square forward (two squares on its first move); captures diagonally |
Each piece has a role. Knowing how to use them effectively is key. The opening, middle game, and endgame phases each have distinct strategies. Learning these will improve your game.
The Chessboard
The chessboard is the heart of the game of chess. Understanding its layout and notation is essential for beginners. This knowledge helps players communicate moves and strategies effectively. Let’s break down the key elements of the chessboard.
Board Layout
The chessboard consists of 64 squares. These squares alternate between two colors: black and white. The board is set up with eight rows and eight columns. Each player starts with their pieces on the two rows closest to them.
The bottom-right corner square of the board should always be white. This simple rule helps ensure the board is set up correctly. Here is a table to visualize the layout:
| A8 | B8 | C8 | D8 | E8 | F8 | G8 | H8 |
| A7 | B7 | C7 | D7 | E7 | F7 | G7 | H7 |
| A6 | B6 | C6 | D6 | E6 | F6 | G6 | H6 |
| A5 | B5 | C5 | D5 | E5 | F5 | G5 | H5 |
| A4 | B4 | C4 | D4 | E4 | F4 | G4 | H4 |
| A3 | B3 | C3 | D3 | E3 | F3 | G3 | H3 |
| A2 | B2 | C2 | D2 | E2 | F2 | G2 | H2 |
| A1 | B1 | C1 | D1 | E1 | F1 | G1 | H1 |
Coordinates And Notation
Each square on the chessboard has a unique coordinate. The columns are labeled A through H, and the rows are numbered 1 through 8. This system is known as algebraic notation. For example, the bottom-left square is A1, and the top-right square is H8.
Knowing these coordinates is crucial for recording and discussing moves. For instance, if a pawn moves from E2 to E4, you write it as “E2-E4”. This method is used universally among chess players.
Here is a quick guide to algebraic notation:
- Columns (Files): A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
- Rows (Ranks): 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
Practicing this notation will help you improve your game and understand professional matches.
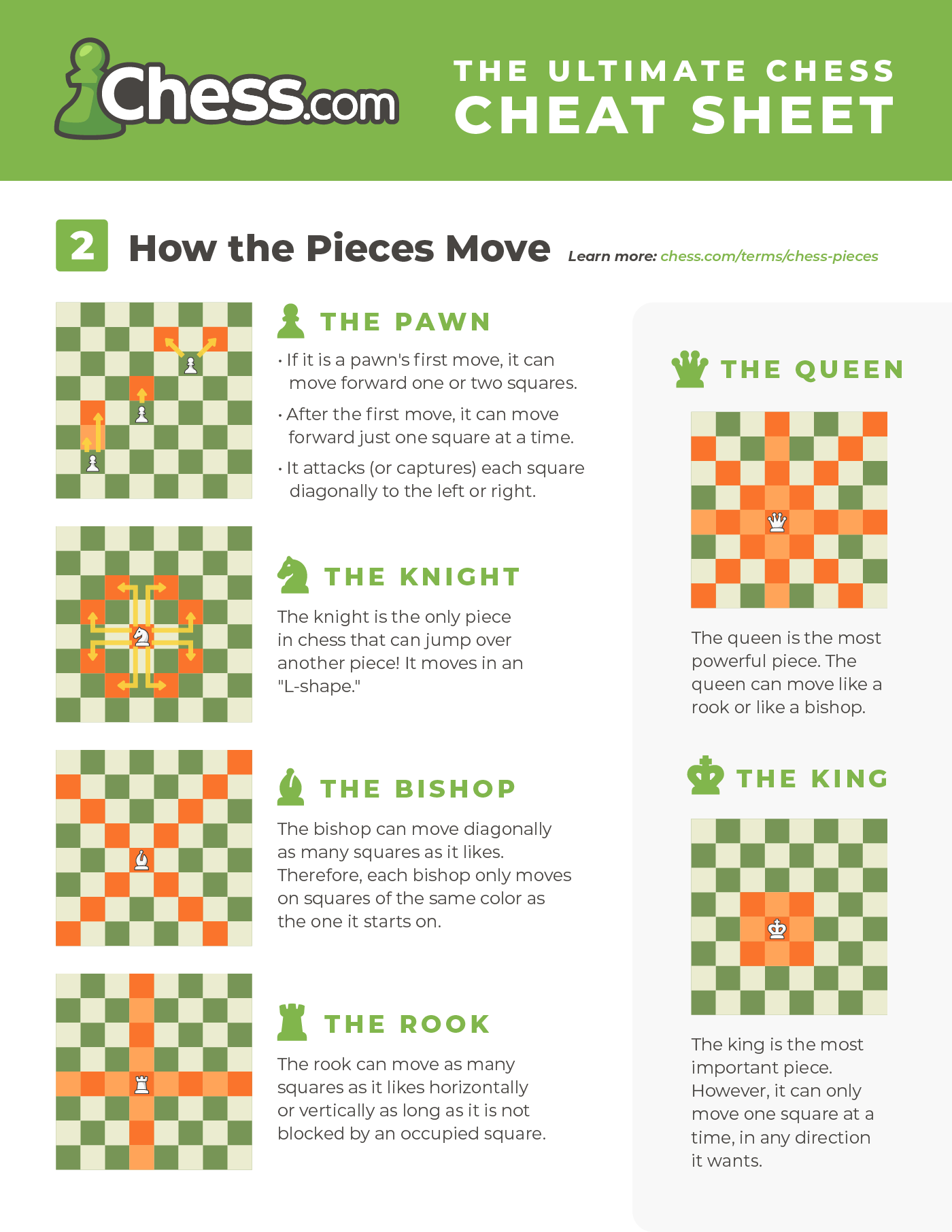
Pawn Movement
Pawns are the most numerous and the weakest pieces on the chessboard. Despite their limited power, pawns play a crucial role in chess strategy. Understanding pawn movement is essential for both beginners and experienced players.
Basic Moves
Pawns move forward but capture diagonally. On their first move, pawns can advance one or two squares. After their initial move, they can only move one square forward.
Here’s a quick summary of the basic pawn moves:
- Move one square forward.
- Move two squares forward on the first move.
- Capture one square diagonally forward.
Promotion And En Passant
Pawns have special moves known as promotion and en passant. These moves add depth to the game.
Promotion occurs when a pawn reaches the opposite end of the board. At this point, the pawn can be promoted to any other piece, usually a queen.
Here are the steps for pawn promotion:
- Move the pawn to the last rank.
- Choose a new piece (queen, rook, bishop, or knight).
- Replace the pawn with the chosen piece.
En Passant is a unique capture move. It can only happen under specific conditions.
The conditions for en passant are:
- The opponent’s pawn moves two squares forward from its starting position.
- Your pawn is on the fifth rank.
- Capture the opponent’s pawn as if it moved only one square.
En passant must be performed immediately after the opponent’s move. Failing to do so means you lose the chance to capture.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Rook Strategy
The rook is a powerful piece in chess. It can control entire rows and columns. Understanding rook strategy can give you an edge in the game. This section will cover the basics of rook movement and special moves like castling.
Movement And Captures
The rook moves in straight lines. This means it can go horizontally or vertically. The rook can move any number of squares in a straight line. Look at the table below for a summary.
| Direction | Squares |
|---|---|
| Horizontal | Any number |
| Vertical | Any number |
To capture an opponent’s piece, the rook must land on that square. Rooks are most effective on open files and ranks. Keep your rooks away from the center. Place them on the side to control more space.
Castling
Castling is a special move involving the king and a rook. It helps protect the king. The king moves two squares towards the rook. The rook jumps over the king. This move has a few rules:
- Neither piece must have moved before.
- No pieces between the king and the rook.
- The king must not be in check.
- The squares the king moves over must not be under attack.
Castling can occur on the king’s side (short castling) or queen’s side (long castling). Short castling is often safer. Long castling can give your rook more activity. Use castling to quickly connect your rooks. This can increase their power.
Knight Techniques
The knight is a unique piece in chess. It moves differently than any other piece. Learning knight techniques can give you an edge. This section covers unique movements and fork attacks.
Unique Movement
The knight moves in an L-shape. This can be two squares in one direction, then one square perpendicular. Or it can be one square in one direction, then two squares perpendicular. This L-shape movement allows the knight to jump over pieces. It can reach squares that are not easily accessible to other pieces.
Knights are especially useful in crowded positions. Their ability to jump over pieces can create unexpected threats. This unique movement can also help the knight control key squares. Understanding this movement is crucial for effective knight play.
Fork Attacks
A fork attack is one of the most powerful knight techniques. A fork occurs when the knight attacks two or more pieces at once. This puts the opponent in a difficult position. They can only move one piece, leaving the other piece vulnerable.
Knights are particularly good at creating forks. Their L-shape movement allows them to cover many squares. This can lead to unexpected forks, catching your opponent off guard. Practicing fork attacks can improve your chess strategy significantly.
By mastering these knight techniques, you can enhance your chess game. The knight’s unique movement and fork attacks can give you a tactical advantage.
Bishop Tactics
The bishop is a key piece on the chessboard. It moves diagonally and can travel long distances. Knowing how to use the bishop effectively can change the course of a game. This guide will explore two main tactics: diagonal movements and long-distance control.
Diagonal Movements
The bishop moves along the diagonals of the chessboard. This means it can travel in any direction, but only on squares of the same color. For example, if a bishop starts on a white square, it will always be on white squares.
A bishop can cover a lot of ground quickly. This makes it a powerful piece. It is important to place your bishop where it has the most mobility.
Here is a quick tip: Try to control the center of the board. A bishop in the center can strike in many directions.
Long-distance Control
Bishops can control long distances on the board. This is their unique strength. They can threaten multiple pieces from afar. This can force your opponent to think carefully about their moves.
Let’s look at an example in a table:
| Bishop Position | Controlled Squares |
|---|---|
| d4 | a1, b2, c3, e5, f6, g7, h8, g1, f2, e3, c5, b6, a7 |
| e5 | a1, b2, c3, d4, f6, g7, h8, h2, g3, f4, d6, c7, b8 |
Notice how many squares a bishop can control from a central position. This demonstrates its long-distance power.
To maximize your bishop’s potential, keep it active. Avoid keeping it blocked behind your own pawns. This will limit its movement and control.
Queen Dominance
The queen is the most powerful piece on the chessboard. Her presence can change the flow of the game. Understanding her movement and capabilities is essential. This section explores her dominance in detail.
Versatility In Movement
The queen combines the power of the rook and bishop. She moves vertically, horizontally, and diagonally. This allows her to cover many squares on the board. No other piece has this range of movement. This makes her a versatile attacker and defender.
Powerful Attacks
The queen can launch powerful attacks. Her ability to move in multiple directions makes her dangerous. She can attack multiple pieces at once. This puts pressure on the opponent. Her presence forces the opponent to stay alert.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
King Safety
In the game of chess, the king’s safety is crucial. The king is the most important piece on the board. If you lose your king, you lose the game. This section will guide you on how to keep your king safe. Let’s explore the basic movements and the key concepts of check, checkmate, and stalemate.
Basic Movement
The king moves one square in any direction. This includes forward, backward, sideways, and diagonally. The king’s movement is limited compared to other pieces. This makes its safety even more important. Always keep an eye on the king’s surroundings.
Check, Checkmate, And Stalemate
A king is in check if an opponent’s piece can capture it on the next move. When in check, you must make a move to protect the king. You can move the king, block the check, or capture the threatening piece.
Checkmate occurs when the king is in check, and no legal move can remove the threat. This ends the game. The attacking player wins. Always aim to avoid checkmate.
Stalemate happens when a player has no legal moves left, but their king is not in check. This results in a draw. Understanding these concepts helps in keeping your king safe throughout the game.
Special Moves
Chess has special moves that add an extra layer of strategy. These moves can catch your opponent off guard. Mastering these can give you an edge. Let’s dive into the details.
Castling Details
Castling involves the king and a rook. It’s the only time you move two pieces at once. The king moves two squares towards the rook. The rook then jumps over the king. For this move, both pieces must be untouched. The squares between them should be empty. The king can’t be in check. Also, it cannot pass through or end on a threatened square. Castling can be done on the king’s side or queen’s side.
En Passant Explained
En Passant is a unique pawn capture. It occurs when a pawn moves two squares forward from its starting position. If it lands next to an opponent’s pawn, En Passant can be used. The opponent’s pawn can capture it as if it moved only one square. This must be done immediately after the two-square move. If you wait, the chance is lost. This rule prevents pawns from easily escaping capture.
Advanced Strategies
Understanding advanced strategies in chess can make a big difference. These strategies help you gain an edge over your opponent. Let’s explore some key areas: opening principles and endgame techniques.
Opening Principles
The opening of a chess game sets the stage for the entire match. Here are some key principles to follow:
- Control the center: Focus on controlling the central squares (e4, d4, e5, d5). It gives you more room to maneuver your pieces.
- Develop your pieces: Move your knights and bishops early. This helps in creating a strong position.
- Protect your king: Aim to castle early. It safeguards your king and connects your rooks.
- Avoid moving the same piece twice: This principle helps in optimizing your moves. Develop all your pieces efficiently.
Endgame Techniques
The endgame is the final phase of a chess game. Mastering endgame techniques can turn a likely draw into a win. Key techniques include:
- King activity: In the endgame, the king becomes a powerful piece. Move your king towards the center or to attack weak pawns.
- Pawn promotion: Advance your pawns to the 8th rank to promote them to queens. This increases your chances of winning.
- Opposition: Use your king to control key squares and restrict the opponent’s king. This is crucial in pawn endgames.
- Piece coordination: Ensure your remaining pieces work together. This is essential for checkmating the opponent’s king.
Understanding these advanced strategies can greatly improve your chess skills. Practice regularly and observe these principles to become a stronger player.
Common Mistakes
Even seasoned players can make mistakes in chess. They can cost a game or a valuable piece. Knowing these common mistakes helps improve your skills. Learn to recognize and avoid them.
Avoiding Blunders
Blunders are big mistakes that can change the game. They happen when you move too fast. Always think before you move. Check the board and your pieces. Look at your opponent’s pieces too. Avoid letting your pieces get captured easily. Protect your king at all times. Do not leave it in danger. Make sure your moves are safe.
Learning From Losses
Every loss is a chance to learn. Review your game to see what went wrong. Look at each move you made. Find the mistakes. Think about what you could have done better. Ask experienced players for advice. They can help you see things you missed. Practice what you learn. Play more games to improve.
Credit: www.chess.com
Conclusion
Understanding chess rules is crucial for better gameplay. Keep practicing regularly. Learn each piece’s movement. Remember, strategy evolves with experience. Stay patient and keep learning. Chess is a journey, not a race. Enjoy the process. Happy playing!
chessmantras.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases made through our links.







